Look. Feel. Live. Better
| Overview |
|---|
| Primary Concern |
| Also Known As |
| Common Triggers |
| Appearance |
| Primary Treatment Options |
| Time to See Results |
| Management |
| Common Areas |
| Details |
|---|
| Melasma, Hormonal Pigmentation |
| Chloasma, "Mask of Pregnancy" |
| Hormonal Changes (Pregnancy, Contraceptives), Sun Exposure, Genetics |
| Symmetrical, blotchy brown or greyish patches |
| Combination Therapy, Chemical Peels, Laser Treatment, Topical Agents |
| 4 weeks to 6 months depending on severity and treatment |
| Chronic condition requiring ongoing management & sun protection |
| Cheeks, Forehead, Upper Lip, Nose, Chin |
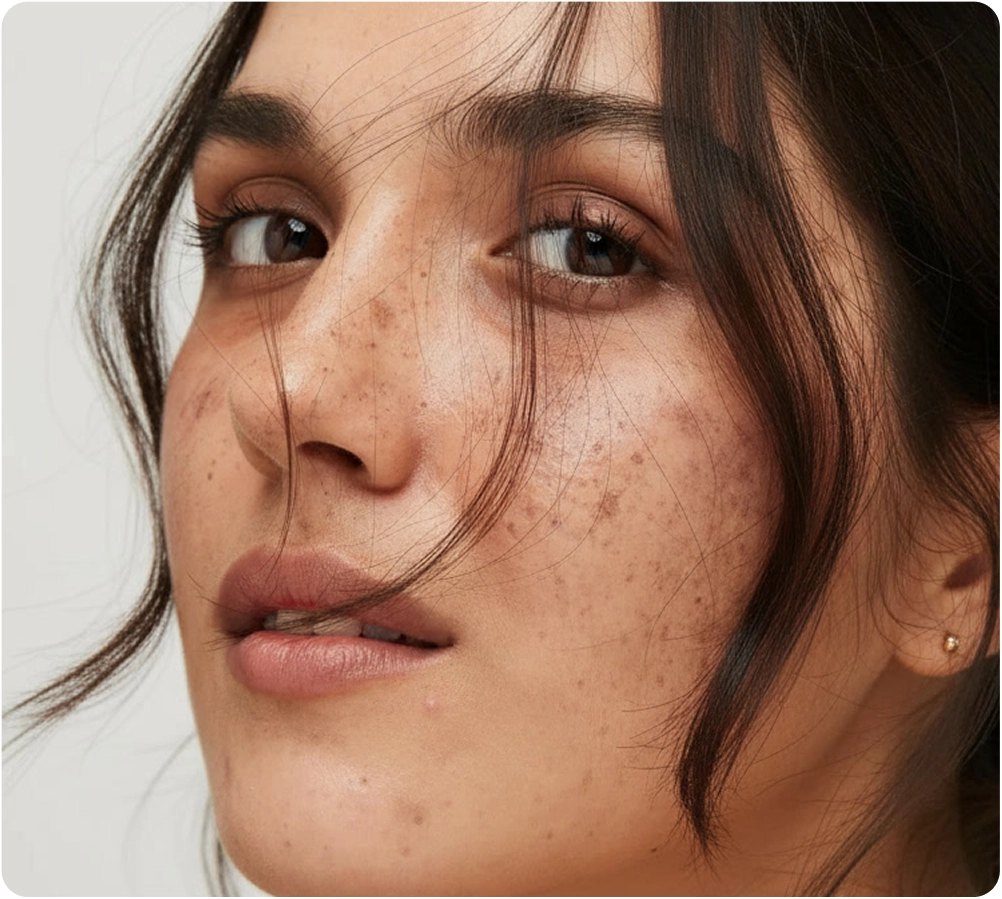
Understanding Melasma
Melasma is a specific and common type of hyperpigmentation that presents as symmetrical, blotchy brown or grey-brown patches on the face. Often called the “mask of pregnancy” or chloasma, it is directly linked to hormonal fluctuations combined with sun exposure.
Unlike sun spots, which are typically small and defined, melasma appears as larger, more widespread patches, creating an uneven and sometimes distressing cosmetic concern.
Finding the best treatment for melasma on the face requires a deep understanding of its triggers and a strategic, long-term approach to management.
Melasma is a complex condition with several contributing factors, but the primary drivers are hormones and ultraviolet (UV) light.
Hormonal Fluctuations are the key trigger. The condition is most common in women, particularly during pregnancy, when taking oral contraceptives, or undergoing hormone replacement therapy. These hormonal shifts stimulate melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) to go into overdrive.
Sun Exposure acts as the activator. Even small amounts of sun exposure can trigger or worsen melasma in individuals who are hormonally predisposed. UV light stimulates the overactive melanocytes to produce excess pigment, causing the characteristic dark patches to appear or darken.
Genetics also play a significant role. If you have a close family member with melasma, you have a much higher likelihood of developing it yourself. Certain skin types are also more susceptible.
Melasma predominantly affects women, with only about 10% of cases occurring in men. It is most common in women aged 20-50 and is particularly prevalent in individuals with olive or darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI). The appearance of melasma on the face—specifically the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip—is the most frequent presentation.

How we at Shumaila’s can treat this
Melasma is a chronic condition that requires a long-term management strategy rather than a one-time cure. At Shumaila’s, our approach focuses on improving overall skin health and supporting the skin’s barrier to help manage pigmentation and prevent flare-ups. We guide our patients towards a holistic plan that includes professional treatments, medical-grade homecare, and diligent sun protection.
Excellent 4.9 out of 5
Non Surgical
First-Line Treatments
Hydrafacial
A gentle Hydrafacial can help improve the overall quality and texture of the skin without causing the inflammation that can trigger melasma. By cleansing, exfoliating, and hydrating the skin, it creates a healthier canvas, which can improve the effectiveness of your topical homecare products.
Ideal for
Maintaining skin health, gentle exfoliation, improving skin radiance
Results
Immediate improvement in skin hydration and glow
Duration
Recommended as part of a regular skin maintenance routine

Profhilo®
Profhilo is a unique injectable treatment that provides intense hydration from within. By remodelling the skin’s structure, it helps to improve overall skin quality and resilience, which is crucial for managing chronic conditions like melasma.
Ideal for
Dehydrated skin, improving skin texture and firmness
Results
Improved skin quality over a course of 2 treatments
Duration
Maintenance sessions are recommended every 6 months
Polynucleotides
Polynucleotides are a cutting-edge bio-stimulator that works at a cellular level to repair and regenerate skin tissue. For melasma, this helps to build a stronger, healthier skin barrier, making it less susceptible to pigmentation triggers.
Ideal for
Compromised skin barrier, cellular-level repair
Results
Gradual improvement in skin health and resilience over 2-3 sessions
Duration
A course of treatments followed by maintenance sessions
Why choose Shumaila’s
for Melasma Treatment?
Frequent Asked Questions
Because the most effective way to treat melasma is usually a personalised combination plan, costs can vary from person to person. Some patients may benefit from standalone treatments such as chemical peels, while others achieve better results with a programme that can include peels, microneedling, and targeted homecare products.
At your consultation, we’ll assess your skin, recommend the most suitable treatment plan, and provide a clear, itemised quote. We’ll always aim to balance effectiveness with your budget.
There is no single “best” treatment. The most effective strategy is almost always a combination approach that includes professional treatments (like peels), medical-grade topical agents (such as tranexamic acid or retinoids), and, most importantly, strict, daily use of a high-SPF, broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Currently, there is no permanent cure for melasma. It is a chronic condition that can be very effectively managed, but not eradicated. Successful long-term management involves consistent treatment and a lifetime commitment to sun protection to prevent flare-ups.
Hydroquinone is a powerful prescription-only skin-lightening agent that can be effective for melasma, but its use is controversial and strictly regulated in the UK. It must be used under medical supervision for short periods due to potential side effects. We prioritise proven alternatives like tranexamic acid, azelaic acid, and specific retinoids that offer excellent results with a stronger safety profile.
Melasma often returns due to its chronic nature and sensitivity to triggers. The most common reason for recurrence is sun exposure—even incidental exposure on a cloudy day can be enough to reactivate the pigment-producing cells. Hormonal shifts can also cause a flare-up. This is why ongoing maintenance and sun protection are non-negotiable.
Treating melasma during pregnancy is challenging as many effective ingredients (like retinoids and hydroquinone) are not recommended. However, we can support you with pregnancy-safe options like azelaic acid-based peels and provide a robust sun protection plan to prevent it from worsening. A full treatment plan can begin after you have finished breastfeeding.
